Bridged AP mode
Overview
By default RaspAP configures a routed AP as its hotspot, where your device creates a subnet and assigns IP addresses to connected clients. If you would rather have your upstream router assign IP addresses, RaspAP lets you change the hotspot configuration to an alternative bridged AP. This is also useful if you want your device and its hotspot clients to be visible to other devices in your router's network.
Use cases
Bridged AP mode is ideal for several scenarios where you may want to extend your existing network rather than create a separate subnet:
- Network extension: Extend WiFi coverage in areas with weak signal by placing your device as a wireless bridge between your router and distant clients
- Unified network: Keep all devices on the same subnet for simplified file sharing, printer access, and network discovery without NAT complications
- IoT integration: Allow IoT devices connected to the AP to communicate directly with other devices on your main network, such as smart home hubs or network storage
- Guest access: Provide wireless access to visitors while maintaining centralized DHCP management and network policies through your main router
- Simplified management: Manage all network settings, port forwarding, and DHCP reservations from a single location (your upstream router) rather than configuring multiple layers of routing
In bridged mode, your device acts as a transparent WiFi access point, with all connected clients appearing as if they were directly connected to your router. This eliminates double-NAT issues and simplifies network architecture at the cost of some advanced routing features available in RaspAP's default routed AP mode.
Enabling bridged AP mode
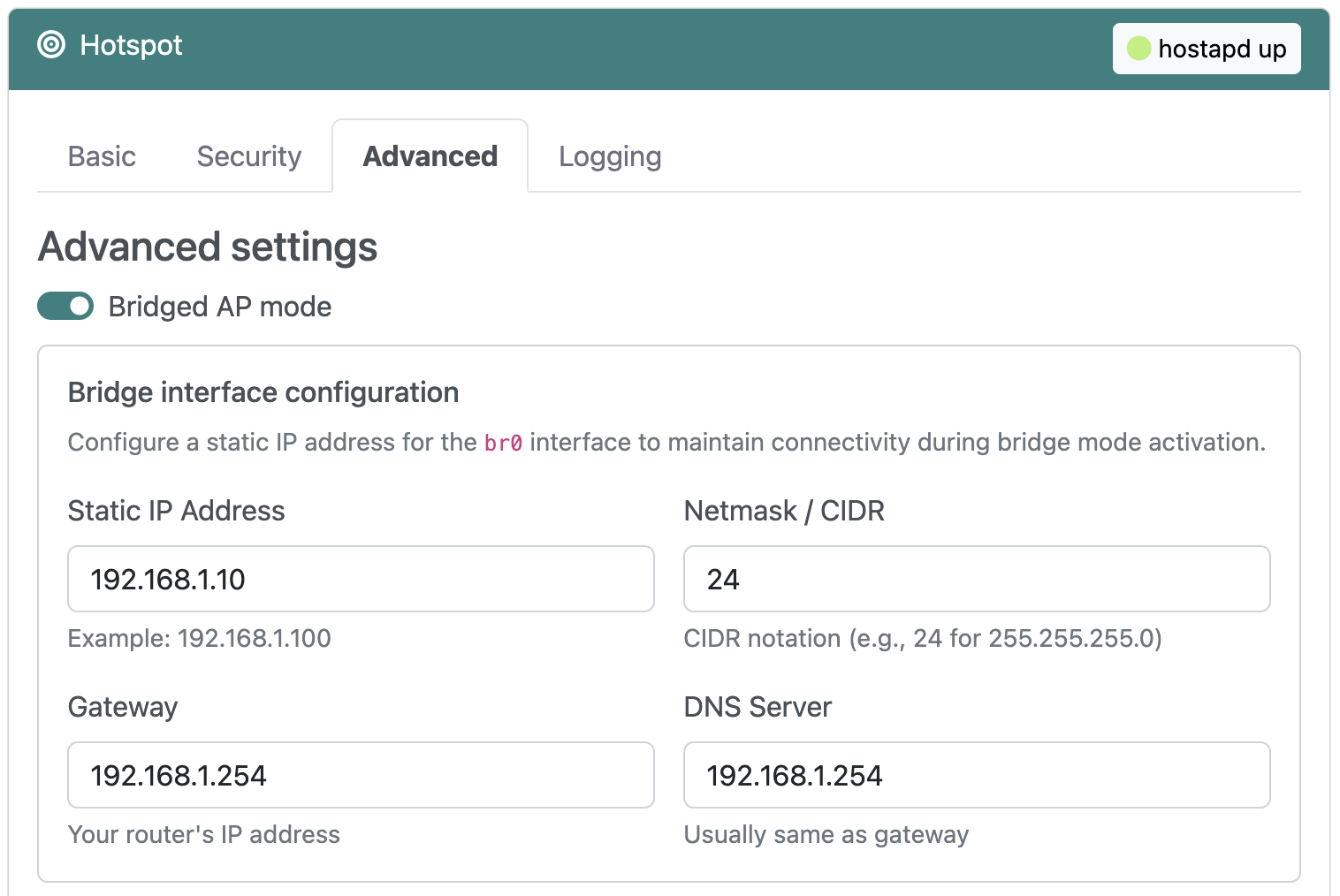
From RaspAP's Hotspot > Advanced tab, select the Bridged AP mode option. When this option is enabled, fields will appear that will allow you to configure a static IP address for the bridge interface.
Configuring a static IP
When enabling bridged AP mode, it's strongly recommended to configure a static IP address for your device. This prevents connectivity issues that can occur when your device requests a new IP address from the upstream router during the transition to bridged mode.
To configure a static IP address:
- Enable the Bridged AP mode checkbox
-
Fill in the Bridge interface configuration fields:
- Static IP Address: The IP address you want assigned to your device (e.g.,
192.168.1.10) - Netmask / CIDR: Network mask in CIDR notation (typically
24for a/24subnet) - Gateway: Your router's IP address (e.g.,
192.168.1.254) - DNS Server: DNS server address, usually the same as your gateway
- Static IP Address: The IP address you want assigned to your device (e.g.,
-
Choose Save settings and then Restart hotspot
Tip
Select an IP address that is outside your router's DHCP range to avoid conflicts with dynamically assigned addresses. For example, if your router assigns DHCP addresses in the range 192.168.1.100-192.168.1.254, choose an address like 192.168.1.50. Consult your router's DHCP settings to determine the appropriate range.
Note
After enabling bridged AP mode with a static IP, access RaspAP's web interface at the IP address you configured (in the example above, http://192.168.1.10). The default 10.3.141.1 address will no longer work.
Limitations
Bridged AP mode operates under some constraints as compared to RaspAP's default routed AP mode. These are discussed below.
WiFi client mode
On the Hotspot > Advanced tab the Wifi Client AP mode option is disabled or "greyed out". The reason for this is your device cannot connect as a client to another wireless network while simultaneously hosting its own bridged access point.
DHCP server
The DHCP Server page is disabled and hidden from the adminstration interface. This is because in bridged AP mode all DHCP functions are delegated to your upstream router. To configure DHCP settings for your network, access your router's web interface.
VPN considerations
Clients connected to a bridged AP with OpenVPN enabled will not have their traffic routed through the VPN server. Your device itself will still have its own traffic routed through the VPN server, however.
Accessing the web interface
With a static IP configuration
If you configured a static IP address for bridged mode, simply access RaspAP's web interface at that address. For example, if you configured 192.168.1.10, navigate to http://192.168.1.10 in your browser.
Troubleshooting
If you are unable to connect clients to your bridged AP, start by following the recommendations in this FAQ. Client connectivity issues in bridged AP mode are most often the result of your upstream router, not RaspAP. For this reason, please check your router's web interface and DHCP settings before reporting a bug.
Discussions
Questions or comments about RaspAP's bridged AP mode? Join the discussion here.